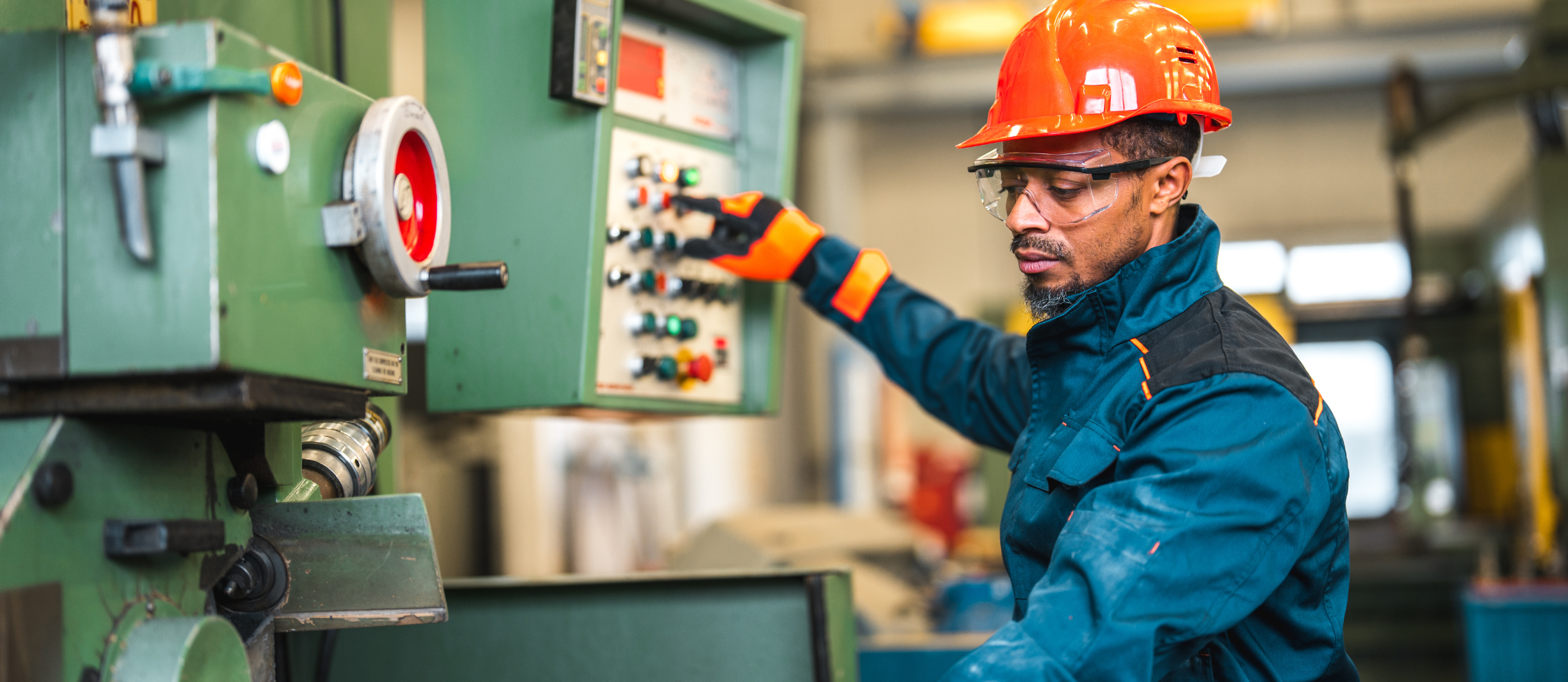
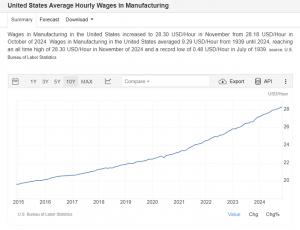
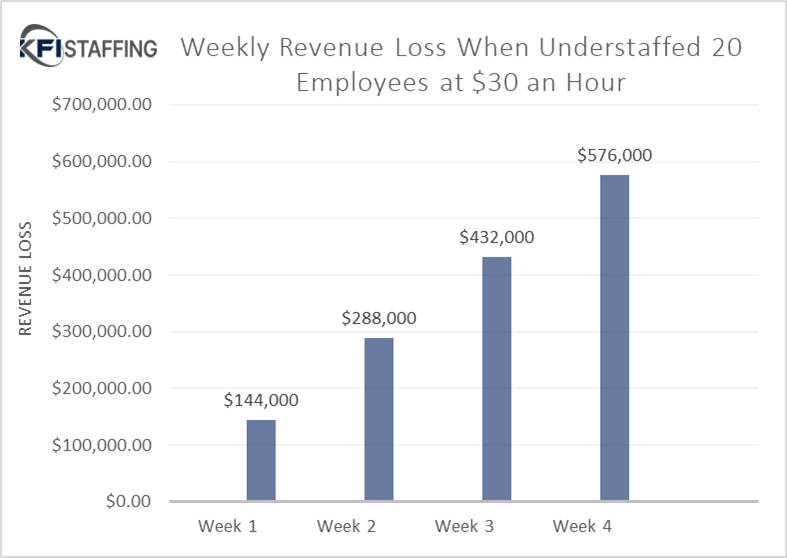
We recognize the significance of machine operator roles in the manufacturing industry. Machine operators assist in maintaining production flow, ensuring that machines run efficiently, and help uphold quality standards. When facilities face understaffing in this area, it can lead to challenges in maintaining productivity on the floor.
The role of a machine operator is a vital part of the manufacturing workforce, where demand remains steady. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 85,500 openings for machine operators are projected each year. With production demand on the rise, this number is only expected to increase.
What Does a Machine Operator Do?
A machine operator’s primary duty is to assist in operating and maintaining machinery in a manufacturing environment. Although the role doesn’t require prior experience, on-the-job training equips workers with the skills to perform their duties. Machine operators ensure machines function properly and assist the team with various stages throughout the manufacturing process.
Some of the typical tasks machine operators may perform include:
- Operating Machines: Assist in the operation of production machinery under supervision.
- Feeding Materials: Load raw materials into machines to keep production moving smoothly.
- Monitoring Machine Performance: Watch machines during operation to ensure they are running correctly.
- Assisting with Minor Repairs: Help troubleshoot and fix basic mechanical issues when needed.
- Maintaining Cleanliness: Keep the work area and machines clean and in good working condition.
Dependent upon the industry, the specifics of the role may vary, but the machine operator’s contributions are crucial to keeping production on track.
Here are a few examples how a machine operators’ tasks could differ based on the specific industry:
Automotive Manufacturing: Operate machinery that produces or assembles parts for vehicles, such as engines, tires, and body frames. Responsibilities include adjusting machine settings, inspecting components for defects, and performing basic maintenance on the machines.
Plastics Manufacturing: Set up and operate injection molding machines or extrusion machinery to create plastic products. A machine operator ensures the machines are functioning properly, loads raw materials, monitors the process, and checks the finished products for quality.
Metal Fabrication: Operate CNC machines, lathes, or milling machines to cut, shape, or weld metal into components or products. Machine operators follow blueprints, make precision measurements, and inspect completed parts for accuracy and quality.
Food and Beverage Manufacturing: Operate machines that process and package food and beverage products. Tasks include mixing ingredients, running bottling or canning lines, monitoring temperature and pressure, and ensuring that safety and quality standards are met.
Packaging Manufacturing: Operate machines used to create packaging materials like cardboard boxes, plastic containers, or bottles. The machine operator loads raw materials, ensures proper cuts or molding, and oversees the packaging process to ensure quality.
Chemical Manufacturing: Operate mixers, reactors, or other equipment to produce chemical products. Operators follow safety protocols, monitor pressure and temperature, and adjust machine settings to control reactions and ensure product quality.
Glass Manufacturing: Operate machines that produce glass products, such as glass containers, windows, or sheets. This can include setting up the furnace, monitoring temperature, and inspecting the final products for quality.
Each industry may require specialized skills and safety procedures, but machine operators across all industries focus on efficiently running machines, maintaining quality control, and keeping production moving smoothly.
What Does the Day-to-Day Look Like for a Machine Operator?
Their responsibilities may include setting up machines, ensuring materials are properly loaded, and watching for any malfunctions during production. If a machine needs adjustment or encounters a problem, machine operators can assist in getting things back on track.
Machine operators may also assist with quality control by ensuring that materials and finished products meet quality standards. They help check for defects and follow safety protocols closely to ensure a safe working environment for everyone on the floor. Cleanliness and orderliness around machines are also part of their responsibilities to ensure that the manufacturing process is not interrupted.
What Skills Do You Need to Become an Entry-Level Production Worker?
- On the Job Training
Most unskilled machine operator roles do not require formal education beyond a high school diploma or equivalent. Companies typically provide hands-on training to get new hires up to speed on the machines and safety protocols.
- Attention to Detail
In entry-level roles, attention to detail is crucial. Machine operators must ensure that machines are loaded properly and running efficiently to avoid errors that could cause downtime or defective products.
- Physical Fitness:
Like other roles in manufacturing, being a machine operator can be physically demanding. This job may involve standing for long periods, performing repetitive tasks, and lifting materials.
- Basic Technical Skills:
While no advanced technical skills are required, familiarity with basic tools and the ability to understand machine functions can be helpful.
- Safety Awareness
Machine operators must always be mindful of potential hazards in the workplace. Using personal protective equipment (PPE) and following safety guidelines is critical for preventing accidents.
- Communication Skills:
Clear and effective communication is vital for collaborating with team members and supervisors. Good communication helps ensure everyone is aligned with production goals and can address any issues that arise.
- Teamwork:
Manufacturing is a collaborative effort. Machine operators must work closely with their team to ensure the production process runs smoothly and efficiently.
Summary
Machine operators play an essential role in maintaining the smooth operation of manufacturing facilities. Their contributions help ensure that machines run efficiently, materials are processed correctly, and quality standards are met. With on-the-job training, physical endurance, attention to detail, and a commitment to safety, unskilled machine operators become key contributors to the success of manufacturing teams.
At KFI Staffing, we help manufacturers find reliable and motivated unskilled machine operators to fill essential positions, allowing operations to run smoothly and efficiently. By addressing staffing challenges, we help create a stable workforce that contributes to increased productivity and morale across the floor.